Arm Holdings (NASDAQ:ARM) is a British company focused on developing and licensing microprocessor architecture and related software. Since its establishment in 1990, Arm has become a key player in the mobile and embedded computing market, closely tied to the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) sector, mobile devices, and wearable electronics technologies.
Originally formed as a collaboration between Acorn Computers, Apple Inc., and VLSI Technology, Arm’s gamble paid off handsomely. The processor architecture initially developed by Acorn for personal computers laid the groundwork for Arm’s first processors. What sets Arm apart from many tech companies is its business model, centered not on manufacturing and selling microprocessors but on licensing its technologies to other companies for chip production based on Arm’s designs. This approach, coupled with Arm’s RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) architecture, inherently offers more energy-efficient solutions compared to traditional CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing) processors, making it an ideal choice for mobile devices where battery life is critical.
Arm processors have become the preferred choice for most smartphone manufacturers, given the dominance of mobile devices in accessing digital content. In 2016, the Japanese SoftBank corporation (TSE:9984) acquired Arm for $32 billion, enabling its continued growth, especially in artificial intelligence and IoT domains. Despite this acquisition, Arm remains a British company headquartered in Cambridge, England, and has been steadily solidifying its position in the market.
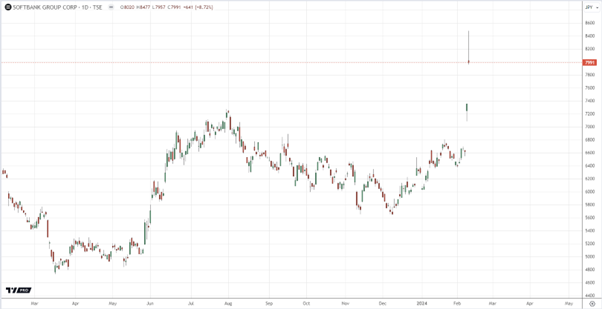
The company regularly releases its financial statements since going public in the United States. On February 7, 2024, Arm announced its quarterly results, instantly catapulting it higher in the list of large-cap companies, making it closer to Microsoft, NVIDIA, and Apple stock. The results surpassed market expectations, with forecasts for the current quarter further driving up stock prices. Consequently, the publication of the quarterly report, which outperformed analysts’ predictions, nearly doubled Arm’s stock price during the trading session, pushing its market capitalization above $116 billion. SoftBank also reaped benefits, witnessing a 15% increase in its share price due to investor optimism.
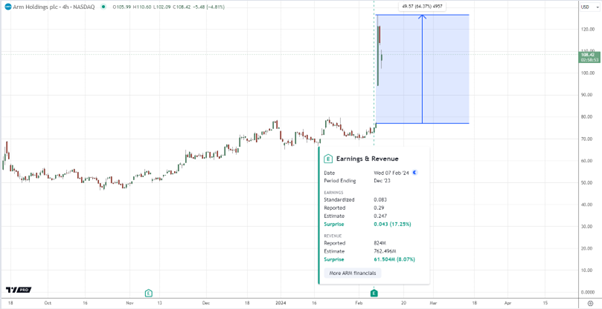
The revenue can be attributed to a resurgence in the smartphone market and the expansion of the more advanced Armv9 architecture, featuring higher deduction rates and more cores per device. Additionally, Arm architecture processors are gaining traction in server and automotive sectors, contributing to increased licensing revenue. Last quarter, Arm’s direct license revenue surged by $354 million, marking an 18% increase.
While SoftBank, holding over 90% of Arm shares, saw a substantial increase in asset value, it’s currently restricted from selling its shares post-IPO. The restrictions are expected to lift in March, enabling SoftBank to capitalize on Arm’s shares. It’s been exactly two years since NVIDIA’s failed attempt to acquire Arm for $40 billion.
For the current quarter, Arm anticipates generating between $850 million and $900 million in revenue, surpassing analysts’ expectations. Operating expenses are projected to remain at $490 million. By the year’s end in April, Arm aims to earn between $3.15 billion to $3.2 billion in revenue, with operating expenses capped at $1.7 billion. Notably, Arm customers shipped 30.6 billion processors over the past year, with smartphone processors contributing to no more than a third of Arm’s revenue, highlighting the company’s successful diversification efforts into other sectors like data centers and automotive.
With continuous innovation and development, each generation of Arm Cortex architecture sees improvements in performance, energy efficiency, and functionality. The company is expanding its reach beyond mobile and consumer devices into servers, supercomputers, and machine learning, ensuring continued growth and relevance in the ever-evolving tech landscape.